The beauty of the Mediterranean diet is that it is not a diet, but the principles of a balanced diet. As a rule, almost any diet implies severe restrictions, it is desirable that it be carried out under the supervision of a doctor and has contraindications. The Mediterranean diet is suitable for everyone, including children, pregnant women and the elderly. Even if you are allergic or intolerant to certain foods, they are easily substituted for others. You will not be hungry and stressed. On the contrary, you will enjoy your food immensely. It is not for nothing that the inhabitants of these regions enjoy excellent health and good character.
As a rule, almost any diet implies severe restrictions, it is desirable that it be carried out under the supervision of a doctor and has contraindications. The Mediterranean diet is suitable for everyone, including children, pregnant women and the elderly. Even if you are allergic or intolerant to certain foods, they are easily substituted for others. You will not be hungry and stressed. On the contrary, you will enjoy your food immensely. It is not for nothing that the inhabitants of these regions enjoy excellent health and good character.
The Mediterranean diet is a lifestyle that allows you to be fit, rarely get sick and prolong youth. Thinking of adapting the diet to a correct diet, he studies the principles of the Mediterranean diet.
In 2010 the Mediterranean diet received the official status of UNESCO as an intangible heritage of the Mediterranean countries: Greece, France, Italy, Morocco, Spain, Croatia, Cyprus, Portugal.
If we go down in history, we can see that in the gastronomic culture of Ancient Greece, and then Ancient Rome, there were already all the main components of this diet. Lots of vegetables and fruits, seafood, olive oil, legumes, limited amounts of meat and sweets. That is, plant foods rich in vitamins, minerals and fiber, high quality proteins, healthy fats and slow carbohydrates. They activate the metabolism, improve digestion, strengthen all functional systems of the body, thanks to antioxidants, slow down the aging process, increase the production of joy hormones, promote beauty and harmony. But the most important thing is that they always allow themselves to be well, but vegetarianism in Mediterranean countries is not very widespread, while there are practically no red meat dishes, other than excessively heavy ones.
Scientists from the Harvard School of Public Health studied the health effects of the Mediterranean diet and concluded that "Mediterranean dietary traditions, regular exercise and smoking cessation can prevent more than 80% of coronary heart disease, 70% of strokes and 90% of type 2 diabetes ".

The term itself appeared in the 50s of the twentieth century, it was introduced by a doctor, a professor at the University of Minnesota Ansel Keys. In 1945 he landed in Italy with a group of American soldiers. By observing locals, Keys found that they were less likely to suffer from cardiovascular problems and had a longer life expectancy than his homeland. He suggested, and later confirmed, that this is the result of a lifestyle and a nutritional system. Shortly before, in the late 1930s, Italian nutritionist Lorenzo Piroddi first linked nutrition and susceptibility to diseases such as diabetes, obesity and bulimia, which is why he is called the "father" of the Mediterranean diet. And Ansel Keys stayed on the coast in Italy and lived up to 100 years.
We list the pros of a Mediterranean diet.
Strengthens the cardiovascular system. Omega fatty acids in olive oil, nuts, seeds, some vegetables and fruits keep blood vessels clean and elastic.
It prevents or treats diabetes, as the diet is dominated by low-glycemic foods and almost no sugar is used, which means fast carbohydrates.
Foods rich in fiber are included in every meal, guarantee a good metabolism, help to gently reduce weight and maintain positive dynamics over time, improve the state of the nervous system, improve mood and stimulate brain activity.
Many foods of the Mediterranean diet favor the synthesis of endorphins, dopamine, serotonin and tryptophan, the so-called happiness hormones. This reduces the risk of developing Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's and dementia in old age.
Chatting with friends, long Sunday family dinners, picnics in nature, cooking together are part of the culture of Mediterranean countries, useful to introduce into everyday life to minimize stress and anxiety levels and strengthen positivity.
Prolongs youth and beauty thanks to flavonoids and antioxidants. They reduce the damage of the oxidative process, which worsens both internal and external conditions. Selenium, manganese, zinc, vitamins A and E make the skin firm and the hair shiny and thick.
There are practically no disadvantages to the Mediterranean diet.
It helps you switch to proper nutrition and improve your health. It is not seasonal, it is not limited in time and implies a varied menu. Its only drawback is the inability to lose weight quickly.
However, in effect, it turns into an advantage. Dramatic weight loss is often traumatic for the body: from a sudden change of regimen, a tangible loss of the usual daily calorie intake, we experience stress. The body responds with poor health, a decline in strength, immunity and mood, chronic diseases worsen or new ones appear if the diet is not controlled.
Yes, for some time the weight goes away quickly, but the brain activates the mode of protection against possible hunger, and even from low-calorie food the body manages to store reserve fat. Therefore, very often after the end of the diet, the weight returns and sometimes even increases.

This will not happen with the Mediterranean diet. You won't see quick changes, but be patient. You will notice the first results in a couple of months. You should eat five times a day in small portions, so you won't feel hungry and your body will receive the full range of nutrients it needs. Gradually, a rational diet will restart the functional systems of the body, metabolism will improve, and weight will return to normal. Add physical activity, at least long walks and the effect will be noticeable.
The list of approved products is extensive. Nutritionists have identified them in a pyramid based on sources (60%) of complex carbohydrates, high-quality fats and vegetables. The former include whole grains, durum wheat pasta, whole wheat bread, nuts and seeds, and legumes. Products from this group should be included in the menu every day.
Vegetables are presented in all varieties. Look especially for leafy greens such as spinach and kale, and vegetables with a minimum of starch such as eggplant and zucchini, cauliflower and broccoli, tomatoes, peppers and fennel. The daily intake of vegetables recommended by the WHO - 6 servings a day - is based on the quantity of vegetables in the Mediterranean diet.
Previously, when there were no modern technologies for preserving vegetables, cooking was based on the principle of seasonality. Alas, in our conditions, seasonal vegetables are a short-lived pleasure. There is a solution: use frozen vegetables. Unlike imported ones, quick freezing, done within a few hours of harvesting at the peak of maturity, preserves almost all the vitamins in them. In winter and spring, the freshness of vegetables is a rather arbitrary concept. Manufacturers take into account the long journey and storage, for which they treat them with chemicals.
Chickpeas, lentils and beans contain complete plant proteins, a rich complex of nutrients and fiber. They saturate well and create a feeling of satiety for a long time. A wide variety of balanced meals can be prepared in combination with vegetables and legumes. Thick, rich soups will keep you warm in cold weather, and salads are a great dinner option. Try eating vegetables and legumes for dinner two or three times a week.

Jasmine rice with chickpeas, mini broccoli, mini cauliflower and truffle oil
Ingredients:
- Chickpeas (chickpeas) Bonduelle 1 can (310 g).
- Bonduelle mini broccoli 1 pack (300 g).
- Mini Bonduelle of cauliflower 1 pack (300 g).
- Jasmine rice 200 g.
- Basil 40 gr.
- Curry 1 tsp
- Olive oil 20ml.
- Salt to taste.
Recipes:
- Cook the rice according to the instructions. Add the curry, mix.
- Heat the olive oil in a pan and lightly fry the cabbage and broccoli.
- Combine cabbage, chickpeas and rice, mix. Salt if needed. Garnish with basil leaves before serving.
Pasta is not bad if made with durum wheat semolina: it is low in calories, has a rich vitamin and mineral composition, and is easily digestible. Furthermore, pasta, like cereals, is one of the main sources of B vitamins. Pasta made from unrefined flour gives energy to the body, for example it is recommended to consume it before physical activity.
Of course, all the benefits can be nullified if you accompany the dish with a fatty sauce or serve as a side dish for meat - such a portion has nothing to do with Mediterranean traditions. Light sauces based on olive oil, vegetables, fish and seafood will be the right choice for pasta.
Spaghetti with mini broccoli and pine nuts
Ingredients:
- Pack of broccoli (300 g).
- Spaghetti 250 gr.
- Pine nuts 40 g.
- Olive oil 20ml.
- Ricotta 100 gr.
- Salt to taste.
Recipe:
- Cook the spaghetti until cooked al dente.
- Boil the broccoli according to the instructions.
- Break 100 g of broccoli with a blender. Mix with ricotta and olive oil.
- Season the spaghetti sauce and the remaining broccoli, season with salt and heat in a saucepan over low heat for 2 minutes.
- Fry the pine nuts in a dry pan and sprinkle them on the spaghetti before serving.

Olive oil, the alpha and omega of the Mediterranean diet, is the gastronomic symbol of this region. Olives began to be consumed here thousands of years ago. Untreated, they have a very bitter taste, so they were salted or squeezed out of the oil.
The reason for this is the oleuropein substance, a phenolic compound which, together with omega fatty acids and vitamin E, determines the benefits of olives. Phenols are powerful antioxidants, have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties and fight free radicals. Scientists found that 2-4 tablespoons of olive oil per day significantly reduced the risk of coronary heart disease.
I have come across a mention of Vitamin F, don't be surprised. Many people do not know that essential fatty acids have a common name: vitamin F. These are archidonic, linoleic and linolenic acids. The human body does not produce them and receives them only with food.
But remember that not all olive oil is the same. The best is extra virgin, a cold-pressed oil produced with mechanical processes. Its acidity, that is, the content of organic acids, does not exceed 0. 8%. During the production process, this oil completely retains vitamins and antioxidants, and should be stored in dark glass bottles at room temperature. It does not need to be heat treated.
Add olives everywhere: in salads, soups, main courses, cakes, toast or in an omelette. Olives have a salty taste, with them the dishes do not require additional salting, which will reduce the amount of salt consumed. Look for inspiration in our selection of recipes with olives.
The second step of the pyramid is the sources of the correct protein, which is 30% in the Mediterranean diet. A part of the body receives proteins from plant foods, most of it from fish and seafood, natural yogurt, ricotta, low-fat cheeses (cheeses made from goat and sheep milk are particularly popular), white meats (chicken, turkey, rabbit) and eggs. Foods in this group should be eaten three to four times a week.
Fish should be eaten not only on Thursday, as the Book of Tasty and Healthy Foods bequeathed, but several times a week. If you choose between river and sea, choose the latter and the fatty varieties. With it, you will receive not only proteins, but also Omega 3 acids, iodine, which is rarely found in food and an excellent complex of vitamins: vitamins A, E, D, C, B. dense structure of muscle fibers. Therefore, they immediately begin to be digested, which makes fish an ideal dietary product.
Talking about fish often leads to complaints that it is expensive and that it is almost impossible to buy good fish. Let's clear up these exciting questions.
In fact, few people manage to buy freshly caught fish. In this case, as with vegetables, don't be afraid to freeze. Respect the rules of defrosting: on the lower shelf of the refrigerator, which will take 10-12 hours and will retain all the nutrients. Also in this case, as for vegetables, at the time of purchase make sure that there are no ice crystals in the package. They are proof that the fish was stored incorrectly: the temperature regime was not observed. Don't even freeze the fish alone.
Fish in all countries is an expensive product, but here too there is a way out. You can't afford salmon or tuna fillets, buy cheaper varieties: cod, mackerel, pink salmon, herring, halibut, flounder, saury, sardines. In principle, in Mediterranean countries, most families cook with these types of fish, dishes with them are very tasty and varied. Many people ignore canned tuna, but in vain: it's much cheaper than fresh and just as healthy if it's not made in oil, but in its own juice. Cooking salads with him is a pleasure: there is no need to worry about the cut.
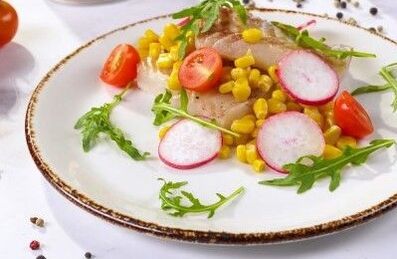
Cod fillet with corn
Ingredients:
- Young Bonduelle corn can 1/3 (140 g).
- Cod fillet 200 g.
- Radish 2 pcs.
- Cherry tomatoes 5 pcs.
- Lemon zest 2 pinches.
- Lemon juice 1 tsp
- Any vegetables to taste.
- Rocket for serving.
- Salt and pepper to taste.
Recipe:
- Dry the cod fillets, bone with tweezers and place the fish in a pan. Then lightly sprinkle with lemon juice, rub with a mixture of salt and pepper spices and lemon zest. Bake at 180 degrees for 15-25 minutes depending on the size of the fillet.
- Cut the cherry in half, cut the radish into slices. Chop the herbs.
- Place the finished cod fillet on a serving dish. Place a garnish of corn, tomatoes, radishes and herbs nearby. Garnish with rocket.
The same goes for seafood - we won't be focusing on lobsters, oysters and lobsters, but let's take a closer look at mussels and shrimp. Iodine, selenium, zinc, iron, copper, magnesium - this is not a complete list of the minerals they contain, as well as a low calorie content. Shrimps are rich in vitamin B12 - participates in the production of hemoglobin, and in mussels - vitamin E, which protects cell membranes from destruction.
The last 10% includes red meat, which is recommended to be consumed no more than once a week, animal fats and simple carbohydrates. Try cooking the meat in a delicate way: stewed or baked and fry it without oil, on the grill. Without sweets, life is deprived of sweet joy, but still choose healthy sweets. Use a minimum of sugar, just the natural sweetness of fruit, honey and even vegetables. For example, young corn is sweet in itself, sweets with it are delicious and original, and you can even eat it straight from the can.

Fruit salad with young corn
Ingredients:
- Young Bonduelle Corn 1 can (340 g).
- Blueberries 70 gr.
- Strawberry 70 gr.
- Raspberry 70 gr.
- Orange 1 pc.
- Walnut 80 gr.
- Natural yogurt 400 ml.
Recipe:
- Peel the zest from the orange. Cut the orange into slices.
- Drain the corn can. Mix the corn and berries.
- Chop the nuts and add them to the yogurt, mix.
- Put the fruit salad with the young corn in small bowls, add the yogurt with the walnuts. Serve with a slice of orange.
Finally, a few words about spices.
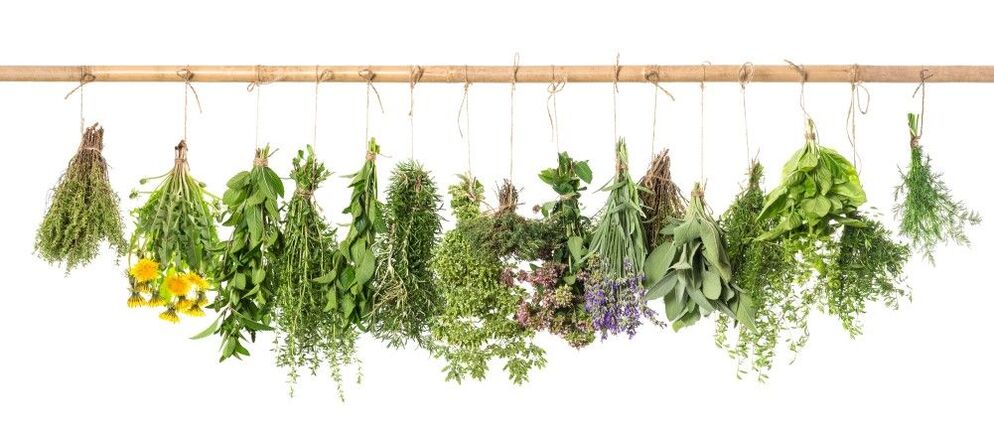
The aromas of solar heat and Mediterranean gardens are contained in rosemary, sage, thyme, marjoram. Parsley and garlic are the simplest and cheapest spices used by the region's chefs for centuries. A mixture of allspice, Provencal or Italian herbs will fill the dishes with interesting meaning and nuances. In addition, they will allow you to use less salt - the brightness of the spices is enough for a full-fledged taste.

There are practically no prohibited foods in the Mediterranean diet and their list coincides with that given by all nutritionists. These are fast food and any "junk" food, industrial semi-finished products, sauces, sweets with preservatives and flavor enhancers.
Drink lots of water, don't neglect a glass of dry red wine (but no more! ) And be healthy!
















































































